Human Interleukin-6 (IL6) Protein, Recombinant
产品货号:PR00167HuM1
$ 询价
规格 100ug
浓度 350ug/ml
产品名称:Human Interleukin-6 (IL6) Protein, Recombinant
状态:Lyophilized
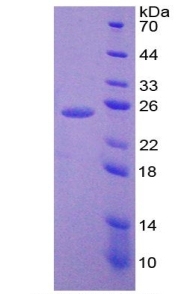
纯度:>97%, by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions and visualized by silver stain.
内毒素:<0.01 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method
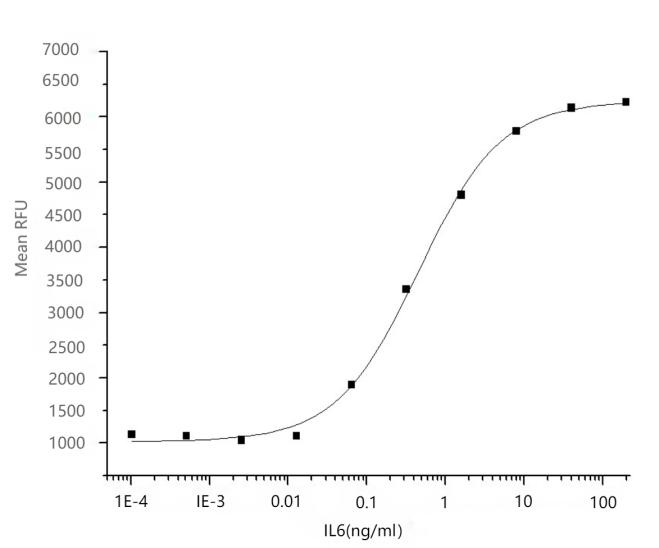
生物活性:The ED50 for this effect is 1-3ng/ml
序列起止:Val30~Met212
Uniprot链接:P05231
宿主:Bacteria
种属:Human
预测分子量:25 kDa
实际分子量:25kDa as determined by SDS-PAGE reducing conditions.
运输方式:This Protein is shipped as lyophilized powder at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended.
稳定性 & 储存条件:Store for up to one year at -20°C to -80°C as lyophilized powder.Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.No activity loss was observed after storage at:-20°C to -80°C for 12 months in lyophilized state;-80°C for 3 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
复溶:Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS and NaCl.Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. Please contact us for any concerns or special requirements.Note:When reconstituting,gently pipet and wash down the sides of the vial .Do not vortex.
质量验证图:
Figure1. SDS-PAGE
For research use only. Not for drug, in vitro, household or other uses.
别称:MGI2-A, MGI2A, HGF, BSF2, HSF, IFNB2, B-Cell Stimulatory Factor-2, Hybridoma/Plasmacytoma Growth Factor, Hepatocyte Stimulating Factor, Cytotoxic T-Cell Differentiation Factor
背景信息:IL-6. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a pleiotropic, alpha -helical, 22-28 kDa phosphorylated and variably glycosylated cytokine that plays important roles in the acute phase reaction, inflammation, hematopoiesis, bone metabolism, and cancer progression (1-5). Mature feline IL-6 is 181 amino acids (aa) in length and shares 56%, 35%, 38%, and 76% aa sequence identity with human, mouse, rat, and canine IL-6, respectively IL-6 (6, 7). IL-6 induces signaling through a cell surface heterodimeric receptor complex composed of a ligand binding subunit (IL-6 R alpha) and a signal transducing subunit (gp130). IL-6 binds to IL-6 R alpha, triggering IL-6 R alpha association with gp130 and gp130 dimerization (8). gp130 is also a component of the receptors for CLC, CNTF, CT-1, IL-11, IL-27, LIF, and OSM (9). Soluble forms of IL-6 R alpha are generated by both alternative splicing and proteolytic cleavage (5). In a mechanism known as trans-signaling, complexes of soluble IL-6 and IL-6 R alpha elicit responses from gp130-expressing cells that lack cell surface IL-6 R alpha (5). Trans-signaling enables a wider range of cell types to respond to IL-6, as the expression of gp130 is ubiquitous, while that of IL-6 R alpha is predominantly restricted to hepatocytes, monocytes, and resting lymphocytes (2, 5). Soluble splice forms of gp130 block trans-signaling from IL-6/IL-6 R alpha but not from other cytokines that use gp130 as a co-receptor (5, 10). IL-6, along with TNF-alpha and IL-1, drives the acute inflammatory response and the transition from acute inflammation to either acquired immunity or chronic inflammatory disease (1-5). When dysregulated, it contributes to chronic inflammation in obesity, insulin resistance, inflammatory bowel disease, arthritis, sepsis, and atherosclerosis (1, 2, 5). IL-6 can also function as an anti-inflammatory molecule, as in skeletal muscle where it is secreted in response to exercise (2). In addition, it enhances hematopoietic stem cell proliferation and the differentiation of Th17 cells, memory B cells, and plasma cells (1, 11).
全称:Interleukin-6 (IL6)
说明书:待上传