产品名称:Anti-VIM Antibody, Mouse Monoclonal, H7F
克隆号:H7F
抗体亚型:/
经验证的应用:/
交叉反应:Predict reacts with: Human/Mouse/Rat
特异性:/
免疫原:/
制备方法:Produced in mouse immunized with VIM, and purified by antigen affinity chromatography.
来源:Monoclonal Mouse IgG
纯化:Immunogen affinity purified
缓冲液:Supplied in PBS, 50% glycerol and less than 0.02% sodium azide, PH7.4
偶联物:Unconjugated
浓度:Liquid
运输方式:This antibody is shipped as liquid solution at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended.
储存条件:This antibody can be stored at 2℃-8℃ for one month without detectable loss of activity. Antibody products are stable for twelve months from date of receipt when stored at -20℃ to -80℃. Preservative-Free. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
图片:
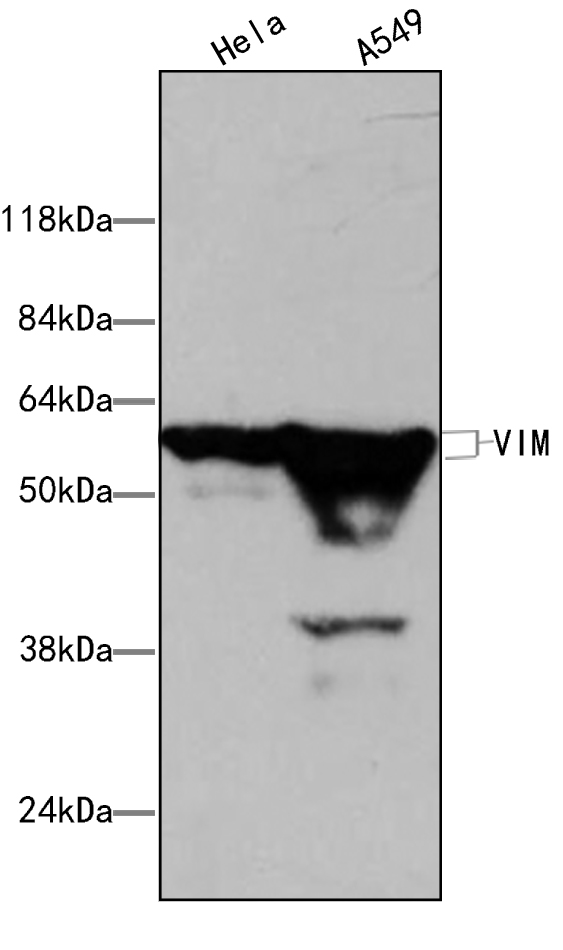
Figure1.Western blot analysis of extracts of various lane1 Hela (+++)、lane2 A549 (++), using VIM antibody (MA00051HuM10-H7F) at 0.5ug/ml Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:20000 dilution. Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST. Detection: ECL Basic Kit . Exposure time: 0.5min.
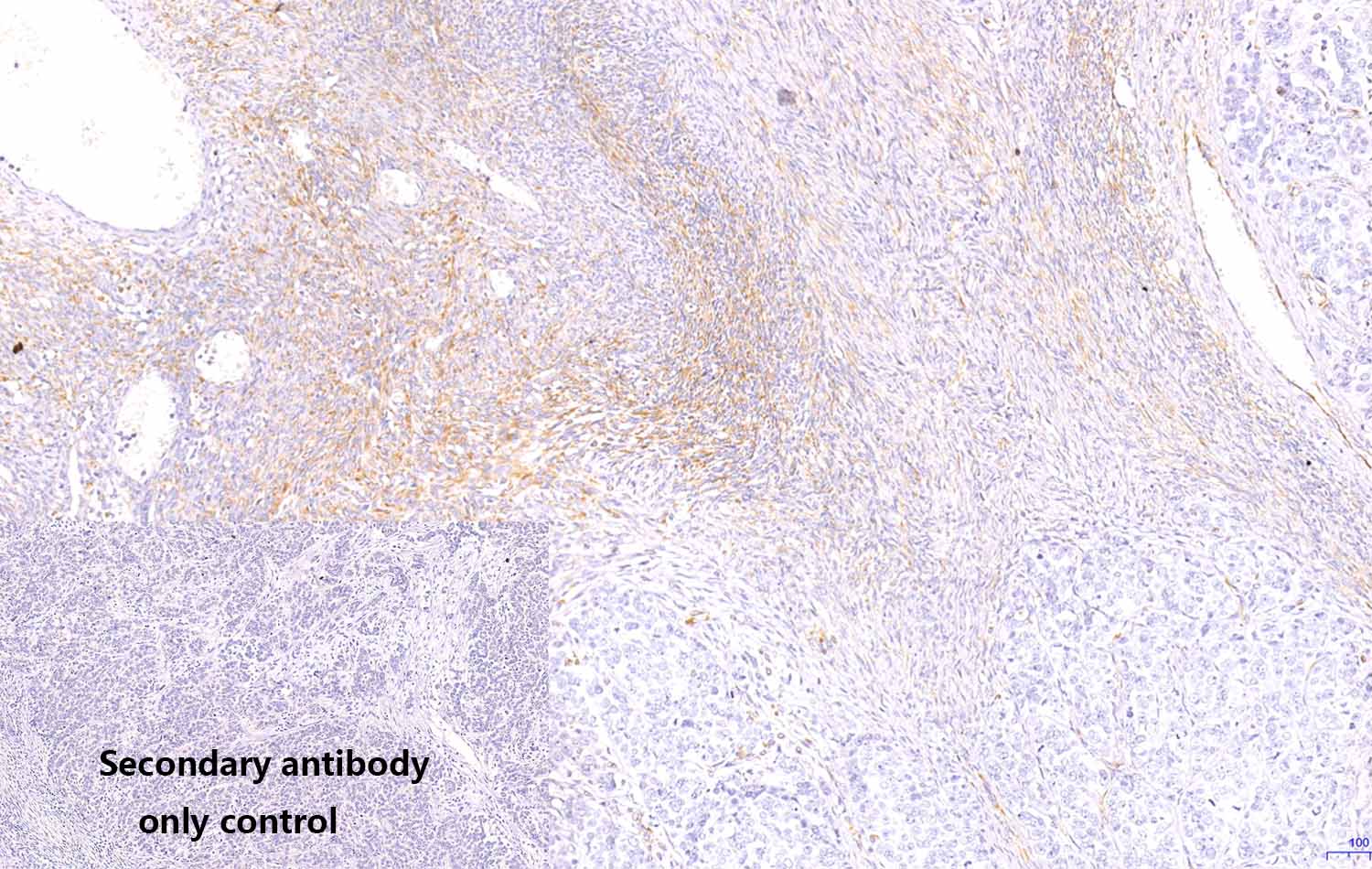
Figure2.Immunohistochemistry (Formalin/PFA-fixed paraffin-embedded sections) analysis of human ovary tumor sections labelling VIM with purified MA00051HuM10-H7F at 5ug/ml dilution . Heat mediated antigen retrieval was performed using Heat mediated antigen retrieval using citrate buffer (PH6.0). Tissue was counterstained with Hematoxylin. Mouse specific IHC polymer detection kit HRP/DAB secondary antibody was used at 1:2000 dilution. PBS instead of the primary antibody was used as the negative control.
别称:CTRCT30, Epididymis luminal protein 113, FLJ36605, HEL113, OTTHUMP00000019224, VIM, VIME_HUMAN, Vimentin.
背景信息:Vimentin. Vimentin is a 57 kDa class III intermediate filament (IF) protein that belongs to the intermediate filament family. It is the predominant IF in cells of mesenchymal origin such as vascular endothelium and blood cells (1-3). The human Vimentin cDNA encodes a 466 amino acid (aa) protein that contains head and tail regions with multiple regulatory Ser/Thr phosphorylation sites, and a central rod domain with three coiled-coil regions separated by linkers (1, 2). Human Vimentin shares 97-98% aa identity with mouse, rat, ovine, bovine and canine Vimentin. Sixteen Vimentin coiled-coil dimers self-assemble to form intermediate (10-12 nm wide) filaments (4). These filaments then anneal longitudinally to form non-polarized fibers that support cell structure and withstand stress (4). IF fibers are highly dynamic, and half-life depends on the balance between kinase and phosphatase activity. For example, phosphorylation followed by dephosphorylation drives IF disintegration, followed by reorganization during mitosis (1, 5, 6). Interactions of head and tail domains link IFs with other structures such as actin and microtubule cytoskeletons (7). Vimentin is involved in positioning autophagosomes, lysosomes and the Golgi complex within the cell (8). It facilitates cell migration and motility by recycling internalized trailing edge integrins back to the cell surface at the leading edge (9-11). Vimentin helps maintain the lipid composition of cellular membranes, and caspase cleavage of Vimentin is a key event in apoptosis (8, 12). Phosphorylation promotes secretion of Vimentin by TNF-alpha -stimulated macrophages (13). Extracellular Vimentin has been shown to associate with several microbes, and appears to promote an antimicrobial oxidative burst (13, 14). Cell-associated Vimentin can also interact with NKp46 to recruit NK cells to tuberculosis-infected monocytes (15).
全称:Vimentin (VIM)